Let’s say you have a users table and a shows table. A user has_many shows and a show can have_many users. You’d need to set up a join table for this.
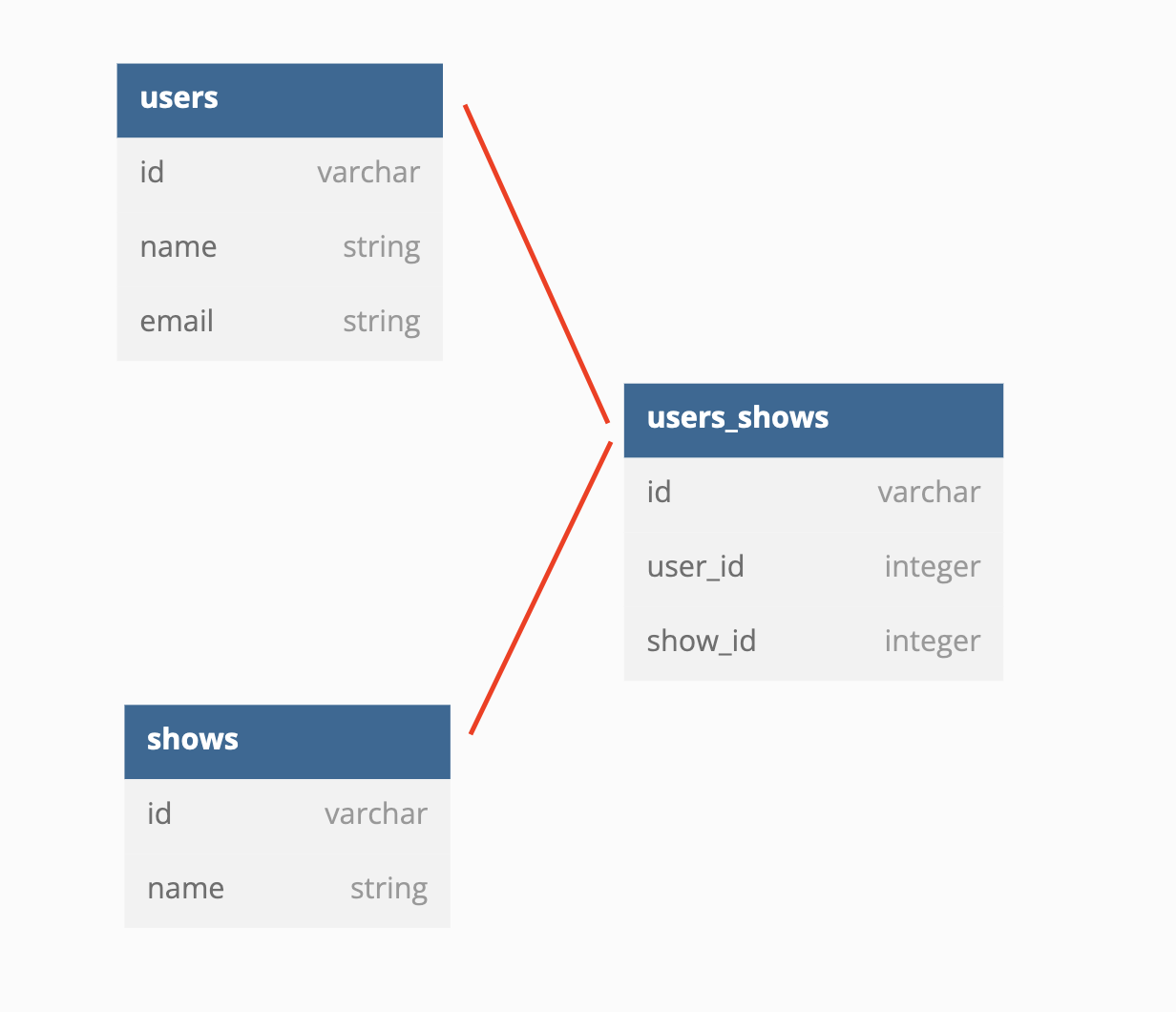
In our example, we’ll first generate a join table migration by running rails generate migration add_users_shows_join_table in the terminal.
class AddUsersShowsJoinTable < ActiveRecord::Migration[7.0]
def change
create_table :users_shows do |t|
t.references :user
t.references :show
end
end
end
I’d rather use a has_many :through association. I’m going to create a model for the users_shows table. The tricky part is that the model has to be singular. The table is users_shows but the model has to be called users_show.rb.
# users_show.rb
class UsersShow < ApplicationRecord
belongs_to :user
belongs_to :show
end
# user.rb
class User < ApplicationRecord
has_many :users_shows
has_many :shows, through: :users_shows
end
# show.rb
class Show < ApplicationRecord
has_many :users_shows
has_many :users, through: :users_shows
end
